Strengthening Ireland's Digital Economy: An AI Approach to Data Protection and Regulatory Compliance
July 08, 2024 - SelfcomplaiExecutive Summary
The digital transformation of the Irish economy, coupled with its role as a major European technology hub, has significantly amplified the criticality of robust data protection and regulatory compliance. Non-compliance is not merely a theoretical risk; it carries substantial and quantifiable financial penalties, severe reputational damage leading to loss of customer trust, and disruptive operational consequences. Irish businesses, face unique and complex challenges in navigating this regulatory landscape, often struggling with manual, resource-intensive compliance processes. SelfCompl.ai, an AI-powered compliance agent system, offers a transformative approach. By leveraging multi-agent artificial intelligence (AI), it aims to achieve up to an 80% reduction in manual compliance effort, enhance risk mitigation, and ensure audit-level output quality.SelfCompl.ai represents a strategic investment for Ireland, fostering a compliant, secure, and competitive digital economy by turning regulatory adherence into a distinct advantage.
1. Introduction: The Imperative of Data Protection in Ireland's Digital Economy
Ireland's Digital Leadership
Ireland's position as a European hub for multinational technology companies and its thriving business landscape underscore the reliance on data. This digital intensity makes data protection a cornerstone of economic stability and international reputation, not just a legal obligation. The increasing volume of data traffic, driven by cloud adoption and demand for hyperscale facilities, is evident in the projected growth of the Irish data center market. This market was valued at US$3.32 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach US$4.22 billion by 2029, growing at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 4.06% (Arizton, 2024). Another projection indicates a CAGR of 5.47% during 2023-2028 for the Ireland Data Center Market (Business Wire, 2023). This significant growth directly correlates with the increasing volume of personal data being processed within the country, highlighting the expanding scope of data protection needs.
Foundational Regulatory Frameworks: GDPR
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), directly applicable across the European Union (EU) since May 2018, sets a high global standard for data privacy. It impacts any organization processing personal data of EU residents, regardless of the organization's physical location (DLA Piper, 2025); (George, 2025). This broad applicability means that a vast array of businesses operating in or interacting with the EU are subject to its stringent rules. Complementary ISO standards, such as ISO 9001:2015 for Quality Management and ISO 27001 for Information Security, are crucial for establishing robust organizational processes and security frameworks that underpin comprehensive GDPR compliance. These standards provide a structured approach to managing quality and information security, which are foundational to protecting personal data effectively.
Purpose of the Report
This report aims to comprehensively detail the significant and escalating challenges faced by Irish businesses in achieving and maintaining compliance with these complex data protection regulations. It will demonstrate the substantial market demand for advanced compliance solutions and introduce SelfCompl.ai as an innovative, AI-powered paradigm designed to transform compliance from a burdensome obligation into a strategic competitive advantage. By outlining the problems and presenting a viable solution, the report seeks to inform stakeholders about the critical need for modern compliance tools in Ireland's evolving digital landscape.
2. Problem Statement: Navigating the Complexities and Costs of Compliance
2.1 The Regulatory Landscape: GDPR Obligations
The regulatory environment governing data protection in Ireland, primarily driven by GDPR, presents a multifaceted challenge for businesses.
Steps by EU to Reduce Administrative Burdens:
Even though on recent EU proposals, published in May 2025, aim to amend GDPR to reduce regulatory burdens for Small Mid-Cap Enterprises (SMCs), defined as organizations with fewer than 750 employees (Data Law, 2025); (O'Dea, 2025). These amendments propose raising the risk threshold for RoPA exemption and removing "occasional processing" limitations, which has been described as a "welcome amendment" to cut "red tape" (Data Law, 2025); (O'Dea, 2025). However, this regulatory simplification does not eliminate the underlying need for robust data protection. For companies supplying to larger enterprise businesses, data protection shifts from merely a "regulatory requirement to a commercial necessity" (O'Dea, 2025). This means that even if a business is legally exempt from certain RoPA obligations due to its size, market demands from larger clients, who themselves operate under strict GDPR rules, will likely impose similar compliance standards on their supply chain.
This dynamic indicates that compliance is evolving beyond mere legal adherence to become a core business enabler and differentiator in the digital economy. Furthermore, organizations meeting specific criteria, such as public authorities or those engaged in large-scale systematic monitoring or processing of sensitive data, must appoint a Data Protection Officer (DPO) (DLA Piper, 2025). This requirement adds a significant human resource and expertise demand, especially for smaller or less mature organizations.
2.2 The Tangible Costs of Non-Compliance
The consequences of failing to comply with GDPR are severe and extend far beyond abstract legal principles.
Analysis of Significant Financial Penalties:
GDPR fines can reach up to €20 million or 4% of a business's global annual turnover, whichever is higher, for severe violations. Less severe infractions can still incur fines of up to €10 million or 2% of global turnover (Nambiar, 2025); (George, 2025). These penalties are explicitly designed to be "effective, proportionate, and dissuasive," ensuring that non-compliance is a costly mistake (Nambiar, 2025). Ireland's Data Protection Commission (DPC) has solidified its position as a leading enforcer of GDPR compliance within Europe. This is largely due to the presence of numerous tech giants' European headquarters in Ireland, making the DPC the lead supervisory authority for many of these large companies (Colleary, 2025); (Clarke, 2025). In 2024, the DPC issued 11 finalized inquiry decisions, resulting in administrative fines totaling €652 million (Data Protection Commission, 2025); (DataBreaches.Net, 2025); (IAPP, 2025). Since May 2018, the DPC has imposed fines totaling €3.5 billion, a figure that significantly surpasses those levied by other European regulators (Coker, 2025); (Clarke, 2025). The fines are tabulated below:
Table 1: Key GDPR Fines Issued by the Irish DPC (2020-2024)
| Company | Fine Amount (€) | Date of Fine | Reason for Fine |
|---|---|---|---|
| Meta Platforms Ireland Ltd. | 1.2 billion | May 2023 | Illegal data transfers to the U.S. |
| 310 million | Oct 2024 | Processing personal data in advertising practices | |
| Meta Platforms Inc. (FB) | 251 million | Dec 2024 | 2018 data breach impacting 29 million accounts |
| Meta Platforms Inc. (Insta) | 405 million | Sep 2022 | Mishandling children's personal data |
| WhatsApp Ireland Ltd. | 225 million | Sep 2021 | Lack of transparency in data sharing |
| TikTok Technology Limited | 345 million | Sep 2023 | Violations related to children's data processing |
Sources: Data Protection Commission, 2025; Colleary, 2025; George, 2025; De Chazal, 2025; Coker, 2025; Lindberg, 2025
While the DPC has imposed substantial fines, it has also faced criticism for perceived "notorious
laxity,"
delayed investigations, and a reliance on "amicable settlements" (De
Olazabal, 2025). Some commentators suggest this has made it a "significant bottleneck for
enforcement," potentially enabling tech giants to evade meaningful compliance for extended periods (De Olazabal, 2025).
This situation presents a complex
regulatory
environment where the consequences of non-compliance (fines) are severe, but the path to enforcement can
be
prolonged and complex. This dynamic reinforces the imperative for companies to implement robust,
proactive
internal compliance systems. If regulatory oversight is inconsistent or slow, organizations cannot
afford to
be reactive; they must have their own mechanisms to identify and mitigate risks before they escalate to
the
point of DPC intervention, thereby avoiding the high costs and disruptions associated with formal
enforcement actions.
Impact of Reputational Damage and Loss of Customer Trust:
Beyond financial penalties, GDPR non-compliance can severely impact a business's reputation, leading to a significant loss of customer trust and confidence (Nambiar, 2025); (George, 2025); (Neumetric, n.d.); (Sadoian, 2025). Publicized fines and enforcement actions damage brand credibility and deter potential customers and partners who prioritize data privacy (George, 2025). Surveys indicate a strong consumer concern for data privacy: 70% of those surveyed trust the DPC to uphold their rights (Data Protection Commission, 2025), and 2 out of 3 people would trust an organization "a lot less" if it misused personal data (Data Protection Commission, 2025). Critically, 70% of consumers would stop shopping with a brand after a security incident (Vercara, 2024); (Doerer, 2025). While consumer apathy towards breaches increased slightly in 2024 (58% impact on trust, down from 62% in 2023), the fundamental impact on a business's bottom line remains severe, as a significant portion of customers are willing to disengage from brands that fail to protect their data (Vercara, 2024); (Doerer, 2025).
Operational Disruptions and Legal Costs:
Investigations and enforcement actions by regulatory authorities can significantly disrupt business operations, requiring substantial resources to address compliance gaps and implement necessary changes (Nambiar, 2025); (George, 2025); (Neumetric, n.d.); (Sadoian, 2025). This can lead to delays, financial strain, and diverted focus from core business activities (George, 2025). Non-compliance also exposes businesses to potential legal challenges, including class-action lawsuits from affected data subjects seeking compensation for material or non-material damages (Nambiar, 2025); (George, 2025); (Neumetric, n.d.). Defending against these actions incurs substantial legal fees, further draining organizational resources (Nambiar, 2025); (Neumetric, n.d.).
Emerging Focus on Personal Liability:
A growing trend in GDPR enforcement is the focus on personal liability, with regulators examining the roles of individual company directors in data protection violations (Coker, 2025); (Clarke, 2025). This shift suggests that future enforcement may increasingly target not only organizations but also their leadership, adding another layer of risk for executives.
3. Market Analysis: The Growing Demand for Compliance Solutions in Ireland
3.1 The Expanding RegTech and Privacy Management Software Market
The increasing complexity and costs associated with data protection compliance have fueled a rapidly expanding market for technological solutions designed to assist businesses.
Global and European Market Growth:
The global RegTech market is experiencing rapid growth, valued at US$16.18 billion in 2024 and projected to reach US$33.81 billion by 2029, with a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 15.6% (ResearchAndMarkets.com, 2025). Similarly, the global Privacy Management Software market is expanding significantly, estimated at US$3.72 billion in 2025 and expected to reach USD 21.17 billion by 2032, exhibiting a CAGR of 28.2% (Rai, 2025). Europe is a key player in this growth, being the second-largest region in the global data privacy software market, projected to grow at a CAGR of 41.2% during 2023-2030 (Fortune Business Insights, 2025). The European privacy management software market alone is expected to reach US$1,413.4 million by 2030, with a CAGR of 21.8% from 2025 to 2030 (Horizon Grand View Research, n.d.).
Ireland's Specific RegTech Market:
Ireland's domestic market for compliance solutions mirrors this global trend, demonstrating robust expansion. The RegTech industry in Ireland is forecast to grow by 28.7% annually, reaching US$335.27 million in 2024. It is expected to grow steadily at a CAGR of 18.7% US$790.67 million by 2029 (ResearchAndMarkets.com, 2024). This indicates a strong and expanding domestic demand for sophisticated compliance tools.
Drivers of Market Growth:
Several factors are propelling the growth of the RegTech and privacy management software markets:
- Increasing Data Breaches and Fines: The significant financial penalties imposed for non-compliance, as detailed in Section 2.2, directly contribute to the demand for data governance, data mapping, and data management services. Businesses are increasingly investing in these services to reduce the number of breaches and protect sensitive information, viewing them as a necessary safeguard against costly regulatory actions (Straits Research, n.d.).
- Digital Transformation: The pervasive trend of digitization is a major catalyst for the RegTech market. Global spending on digital transformation reached USD 1.8 trillion in 2022, marking a significant 17.6% increase over 2021 (ResearchAndMarkets.com, 2025). This includes the widespread adoption of cloud-based services, with European public cloud services spending projected to reach USD 258 billion by 2026 (Fortune Business Insights, 2023). As more operations move to digital platforms and the cloud, the need for automated and robust compliance solutions intensifies.
- Rising Need for Transparency: Consumers worldwide are increasingly demanding greater transparency in how their personal data is processed. This rising demand makes GDPR services crucial for fostering trust between businesses and their clientele. Companies recognize that meeting these transparency requirements is vital for maintaining customer loyalty and avoiding reputational damage (Straits Research, n.d.).
- AI Governance and Integration: The implementation of AI governance across regions is propelling market growth. AI is increasingly integrated into larger solutions to assess privacy impacts and analyze huge datasets (Rai, 2025); (Fortune Business Insights, 2025). The proliferation of AI governance platforms is accelerating organizations' ability to monitor, control, and ensure the ethical use of artificial intelligence, addressing growing regulatory and societal demands for responsible AI deployment (Rai, 2025). The rise of AI presents a dual force: it introduces new compliance complexities, such as ensuring the lawfulness of data used for AI training, managing algorithmic bias, and addressing explainability challenges. Simultaneously, AI-powered solutions are becoming indispensable for managing these very complexities at scale. This creates a self-reinforcing dynamic where the more AI is adopted across various business operations, the greater the need for AI-powered compliance tools to effectively monitor, analyze, and manage the associated data protection risks. This positions advanced RegTech as a crucial enabler for businesses to responsibly adopt AI while remaining compliant with evolving regulations like GDPR and the EU AI Act.
Table 2: European and Irish RegTech & Privacy Management Software Market Forecasts
| Market Segment | Base Year Market Size (USD) | Forecast Year Market Size (USD) | CAGR | Forecast Period |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Global RegTech | $16.18 Billion (2024) | $33.81 Billion (2029) | 15.6% | 2024-2029 |
| Ireland RegTech | $335.27 Million (2024) | $790.67 Million (2029) | 18.7% | 2024-2029 |
| Europe Data Privacy Software | N/A | N/A | 41.2% | 2023-2030 |
| Global Privacy Management Software | $3.72 Billion (2025) | $21.17 Billion (2032) | 28.2% | 2025-2032 |
| Europe Privacy Management Software | $442.5 Million (2024) | "$1,413.4 Million (2030)" | 21.8% | 2025-2030 |
Sources: ResearchAndMarkets.com, 2025; ResearchAndMarkets.com, 2024; Fortune Business Insights, 2025; Rai, 2025; Horizon Grand View Research, n.d.; Straits Research, n.d.
3.2 Sector-Specific Compliance Pain Points in Ireland
While GDPR applies broadly, its implementation presents unique challenges across different sectors in Ireland, each grappling with specific operational realities.
3.2.1 Hospitality and Tourism
The hospitality and tourism sector handles an extensive amount of personal data, including names, contact information, payment details, and even dietary preferences. Ensuring the security of this vast data is paramount for GDPR compliance. A significant challenge arises from the sector's reliance on numerous third-party vendors for services such as online booking systems, payment processors, and customer relationship management (CRM) tools. Ensuring these vendors are GDPR compliant and establishing clear contractual agreements outlining responsibilities is a complex undertaking. Data retention and deletion policies also pose difficulties. GDPR requires organizations to retain personal data only for as long as necessary, which can be challenging when managing reservations, loyalty programs, and historical customer databases. For organizations operating across borders, transferring guest data internationally requires specific safeguards under GDPR, adding another layer of complexity. Furthermore, high staff turnover in the hospitality industry makes consistent training on data protection principles and best practices a continuous challenge. Obtaining clear, unambiguous, and opt-in consent for marketing activities, separate from other terms and conditions, sets a high standard under GDPR. The legal obligation to keep a visitor register for overnight accommodation must be carefully managed to prevent using this data for other purposes without separate consent.
3.2.2 Financial Services
Irish financial institutions operate within a highly complex regulatory environment, encompassing GDPR and various other data privacy laws, which collectively impose significant compliance burdens. The financial sector is the most targeted industry worldwide for cyberattacks, with 23% of global phishing attacks aimed at financial organizations in Q2 2023. This necessitates exceptionally robust cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive financial and personal data. Ireland faces an acute shortage of skilled cybersecurity staff and professionals with specialized skills in data analytics and regulatory compliance. This skills gap exacerbates the challenges faced by the financial sector in maintaining secure and compliant operations. Many financial institutions still utilize outdated legacy systems, which complicate the balance between robust cybersecurity and seamless user experiences, creating vulnerabilities that cybercriminals can exploit. Ensuring that third-party vendors adhere to stringent cybersecurity standards adds another layer of complexity, as financial institutions are often reliant on a network of external service providers. The consequences of non-compliance are severe: cybersecurity breaches can lead to significant financial losses, reputational damage, and legal repercussions. A 2023 survey revealed that 46% of Irish C-suite leaders experienced one or more cyber incidents in the past three years, and 30% faced a data breach.
3.2.3 Technology Sector
The technology sector, especially with its heavy reliance on AI, faces unique challenges in balancing rapid innovation with GDPR compliance. Common pitfalls include ensuring prominent and granular consent notices for data collection, particularly for AI models like chatbots. Data storage also presents difficulties, requiring implementation of retention policies (e.g., auto-deletion or anonymization), maintenance of audit trails for data flow, and provision of user controls for data deletion. Maintaining AI-GDPR compliance necessitates thorough vendor checks, robust contractual protections through Data Processing Agreements, and comprehensive due diligence for AI vendors. Moreover, the ethical usage of AI is pivotal; for decisions heavily impacting individuals (e.g., loans, hiring, insurance claims), human-in-the-loop (HITL) review and documenting AI decision-making processes (explainability) are critical to ensure fairness and accountability.
Ireland's DPC serves as the lead supervisory authority for many major US tech companies under the GDPR's one-stop-shop mechanism. Despite issuing large fines against tech giants, the DPC has been criticized for "notorious laxity," delayed investigations, and reliance on "amicable settlements," which some argue has made it a "significant bottleneck for enforcement". This inaction has allegedly "enabled tech giants to evade meaningful compliance".
This presents a complex and potentially risky environment for the technology sector. While the threat of massive fines is real and impactful, the perceived administrative slowness or reliance on "amicable settlements" might lead to a delayed or insufficient internal compliance response. This creates a situation where companies might be lulled into a false sense of security or face prolonged uncertainty, only to be hit with a large fine later. This dynamic reinforces the imperative for the tech sector to implement proactive, AI-driven internal compliance solutions that are not dependent on the pace or specific focus of regulatory investigations. It highlights that even with a designated lead authority, businesses must take ownership of their compliance posture to avoid both headline-grabbing fines and the operational drag of prolonged regulatory scrutiny.
4. Solution Overview: SelfCompl.ai; A Proactive AI-Powered Compliance Paradigm
4.1 Introducing SelfCompl.ai: An Intelligent AI Co-Pilot
SelfCompl.ai is an AI-powered co-pilot designed to fundamentally transform an organization's approach to regulatory compliance. Its vision is to shift compliance operations from a reactive posture to a proactive one. The primary goal is to establish an intelligent AI Co-Pilot capable of automating a significant portion of security and compliance tasks, aiming for up to an 80% reduction in manual effort and enhanced risk mitigation.
Multi-Agent AI Architecture:
The SelfCompliance Agent will be a modular, multi-agent AI system that orchestrates Large Language Models (LLMs) and tools to guide users through GDPR, ISO 9001:2015, and ISO 27001 compliance. This architecture splits responsibilities across specialized agents, combining high-performance LLMs, lightweight models, and self-automation where necessary, thereby enhancing modularity and security by limiting agent access to only necessary tools.
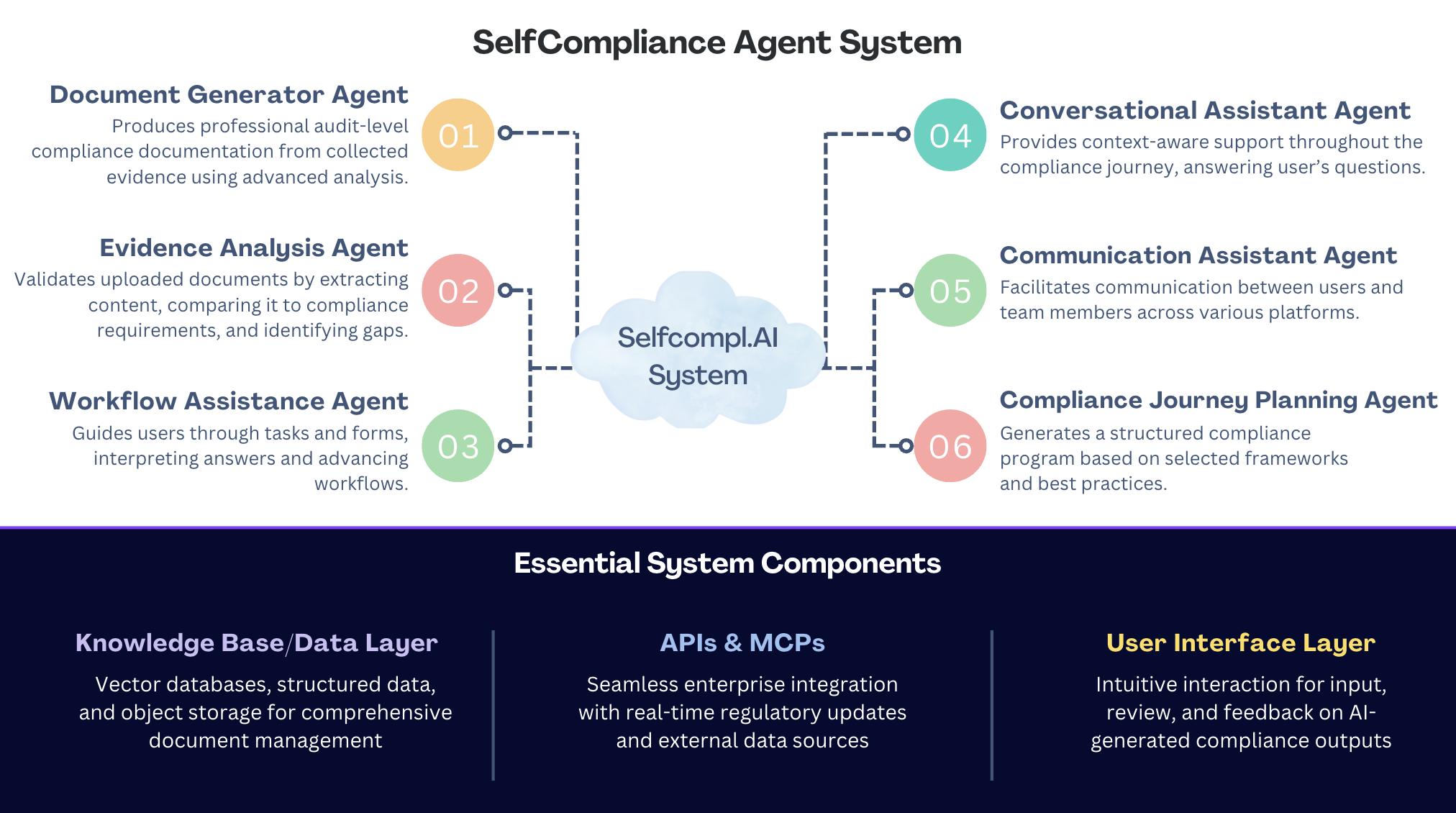
Key Capabilities and Workflow:
SelfCompl.ai offers a comprehensive suite of capabilities designed to streamline and enhance compliance operations:
Automated Task Management
Streamlines time consuming processes like drafting policies, identifying risks, collecting evidence, and preparing reports.Risk Prioritisation and Remediation
AI agents help identify critical risks, assess impact, provide recommendations, and suggest policies to align with requirements.Compliance Monitoring
Provides real-time insights into compliance status and alerts team for any deviations from protocol thus, allowing for immediate corrective actions.Audit Preparation and Reporting
Assists in data collection, analysis and processing for generating comprehensive compliance report, ensuring all necessary information is accurately represented.Compliance Gap Analysis
AI processes large volume of documents, data, and internal logs, comparing with official regulations to precisely highlight deviations and incompleteness. It further prioritises, suggests, and works on necessary fixes and supports continuous improvement.SelfCompl.ai leverages Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) to optimize LLM outputs by consulting a reliable, external knowledge base before generating a response. This grounds LLM responses in verifiable, external knowledge bases, significantly reducing the likelihood of "hallucinations" or plausible-sounding but incorrect information, which is "totally unacceptable in a regulated environment". The system utilizes a robust knowledge base/data layer, storing data in vector databases for high-dimensional embeddings, traditional structured databases for operational data and audit logs, and object storage for raw, unstructured documents. It also integrates with external tools, APIs, and Model Context Protocols (MCPs) to connect with existing enterprise systems and real-time regulatory feeds.
4.2 Addressing Sectoral Pain Points with AI-Driven Solutions
SelfCompl.ai's modular and adaptable design enables it to address the core compliance challenges identified across diverse Irish sectors.
Cross-Sectoral Applicability:
The system's ability to automate tasks, perform gap analysis, and provide real-time monitoring makes it broadly applicable, offering tailored solutions to industry-specific pain points.
Table 3: Sector-Specific GDPR Challenges and SelfCompl.ai's Solutions
| Irish Sector | Key Data Protection Challenges | How SelfCompl.ai Addresses |
|---|---|---|
| Hospitality & Tourism | Vast Data Handling & Retention | Automates classification, retention, and deletion of diverse guest data. |
| Third-Party Compliance | Assesses vendor contracts against compliance, identifies deficiencies. | |
| Staff Training & Awareness | Provides immediate, accurate, always-on guidance for staff, reducing errors. | |
| Financial Services | Complex Regulations & Cybersecurity Threats | Proactively identifies risks, navigates complex rules, suggests mitigation. |
| Cybersecurity & Compliance Skills Gap | Augments human capabilities, reducing reliance on scarce specialized staff. | |
| Legacy Systems Integration | Connects with existing systems for data analysis without full overhaul. | |
| Technology Sector | AI/ML Privacy Challenges (Bias, Explainability) | Provides transparency, human oversight for AI decisions, mitigates bias. |
| Consent & Data Governance for AI Models | Guides implementation of granular consent and data retention for AI data. | |
| Vendor Due Diligence & Contract Review | Assists in reviewing vendor contracts and assessing data protection posture. |
Adaptation to Dynamic Regulatory Changes:
The system's "Model Drift" mitigation strategies, which include continuous model performance review, re-updating the knowledge base, and robust RAG pipeline refreshing mechanisms, ensure it remains aligned with evolving compliance rules and regulations. This continuous adaptation is vital in a rapidly changing regulatory landscape.
4.3 Ensuring Audit-Level Quality and Trustworthiness
Achieving and maintaining audit-level output quality is extremely important for a SelfCompliance agent system operating in a regulated environment. This requires a multi-pronged approach integrating human oversight, transparency mechanisms, and continuous evaluation.
Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) Integration
HITL integrates human judgment into AI workflows for critical outputs. It enables human experts to fact-check, validate AI-generated content, correct mistakes, and provide feedback for continuous learning. This is vital for adapting to new compliance scenarios, improving system reliability, and building trust by ensuring human validation for critical decisions.
Explainable AI (XAI) for Transparency and Auditability
XAI is fundamental for ensuring the transparency and auditability of AI systems, as explicitly mandated by regulations (e.g., GDPR, EU AI Act). It helps demystify AI's "black box" decisions, allowing for understanding and defense of the system's reasoning, meeting model governance requirements, and building trust with regulators and users.
Robust Version Control and Audit Log Trails
Automated version control for all AI-generated and processed content is a cornerstone of auditability and data integrity. It provides irrefutable proof of document state, who (or which AI agent) made changes, when, and why. This is vital for defensibility, regulatory reporting, and internal governance, transforming document management into a proactive, intelligent compliance system.
Continuous Evaluation Metrics
The system employs continuous evaluation using key metrics such as Hit Rate, Mean Reciprocal Rank (MRR), and Relevancy. This ongoing assessment ensures consistent delivery of high-quality, relevant, and accurate responses, maintaining the system's compliance efficacy as models evolve and data changes. This proactive approach mitigates risks like hallucinations and bias, building trust with regulators.
*The strong emphasis on HITL, XAI, and robust audit trails directly addresses inherent skepticism and regulatory concerns surrounding AI's use in sensitive, high-stakes domains like compliance. By building these features into its core design, SelfCompl.ai proactively mitigates risks such as hallucinations and bias, thereby building trust with regulators and users. This is crucial for gaining government acceptance and fostering widespread adoption in regulated sectors.
5. Conclusion: Ireland's Opportunity for Proactive Compliance and Innovation
This report has demonstrated that data protection compliance, particularly under GDPR, represents a significant and escalating challenge for Irish businesses across all major sectors. The tangible costs of non-compliance, ranging from multi-million euro fines to severe reputational damage and disruptive operational consequences, underscore the urgent need for effective solutions. The robust growth of the RegTech and privacy management software markets in Europe and Ireland further confirms a clear and urgent demand for advanced tools to navigate this complex regulatory landscape.
SelfCompl.ai offers a quantum leap in compliance management, transforming it from a reactive, resource-intensive burden into a proactive, strategic advantage. Its AI-powered, multi-agent architecture, combined with features like automated task management, risk prioritization, and comprehensive gap analysis, promises an unprecedented reduction in manual effort and enhanced risk mitigation.
Crucially, the system's inherent design, incorporating Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) integration, Explainable AI (XAI), and robust audit trails, ensures audit-level output quality, transparency, and accountability, directly addressing key regulatory concerns about AI in sensitive domains.
Supporting the adoption and development of innovative RegTech solutions like SelfCompl.ai is not merely about avoiding fines; it is about strengthening Ireland's digital economy, enhancing its global reputation for data protection, and fostering a competitive business environment where compliance becomes a strategic differentiator. By embracing such advancements, Ireland can continue to lead in the digital age, ensuring that its businesses are not only compliant but also resilient, trustworthy, and positioned for sustained growth in an increasingly data-driven world.
References
- Arizton. (2024, July 24). Ireland Data Center Market - Investment Analysis & Growth Opportunities 2024-2029. Retrieved June 23, 2025 from Arizton: https://www.arizton.com/market-reports/ireland-data-center-market-2025
- Business Wire. (2023, August 4). Ireland Data Center Market Growth, Trends, and Forecasts 2023-2028: Increasing Cloud Adoption and Demand for Hyperscale Facilities Bolsters Growth; ResearchAndMarkets.com. From Silicon CAnals: https://siliconcanals.com/ireland-data-center-market-growth-trends-and-forecasts-2023-2028-increasing-cloud-adoption-and-demand-for-hyperscale-facilities-bolsters-growth-researchandmarkets-com/
- Castro, D. (2025, April 7). Europe's GDPR Fines Against US Firms Are Unfair and Disproportionate. From Center for Data Innovation: https://datainnovation.org/2025/04/europes-gdpr-fines-against-us-firms-are-unfair-and-disproportionate/
- Clarke, D. (2025, January 22). GDPR Fines in 2024: A Year of Significant Penalties and Trends. From Truyo: https://truyo.com/gdpr-fines-in-2024-a-year-of-significant-penalties-and-trends/
- Coker, J. (2025, January 21). GDPR Fines Total €1.2bn in 2024. From Infosecurity Magazine: https://www.infosecurity-magazine.com/news/gdpr-fines-total-2024/
- Colleary, K. (2025, June 19). Key takeaways from Ireland's DPC annual report. From Iapp: https://iapp.org/news/a/key-takeaways-from-ireland-s-dpc-annual-report
- Data Law. (2025, May 28). GDPR to update for digital business realities. From Law Society of Ireland Gazette: https://www.lawsociety.ie/gazette/top-stories/2025/may/gdpr-to-update-for-digital-business-realities/
- Data Protection Commission. (2025, June 19). Data Protection Commission publishes 2024 Annual Report. From Data Protection Commission: https://www.dataprotection.ie/en/data-protection-commission-publishes-2024-annual-report
- Data Protection Commission. (n.d.). Case Studies (Annual Report). From Data Protection Commission: https://www.dataprotection.ie/en/dpc-guidance/case-studies-annual-report
- Data protection laws in Ireland. (2025, January 17). From DLA Piper: https://www.dlapiperdataprotection.com/?t=law&c=IE
- De Chazal, E. (2025, June 6). 20 Biggest GDPR Fines of All Time. From Skillcast: https://www.skillcast.com/blog/20-biggest-gdpr-fines
- De Olazabal, I. D. (2025, January 22). Why Ireland is the Achilles Heel of the EU's fightback against Big Tech. From euobserver: https://euobserver.com/digital/arfd2322c4
- Dissent. (2025, June 19). Ireland's Data Protection Commission publishes 2024 Annual Report. From DataBreaches.Net: https://databreaches.net/2025/06/19/irelands-data-protection-commission-publishes-2024-annual-report/
- Doerer, K. (2025, January 10). How cyber incidents impact consumer trust. From CX Dive: https://www.customerexperiencedive.com/news/how-cyber-incidents-impact-consumer-trust/736979/
- EU: EDPB releases 2024 annual report. (2025, April 23). From Data Guidance: https://www.dataguidance.com/news/eu-edpb-releases-2024-annual-report
- Fortune Business Insights. (2025, June 2). Europe Data Privacy Software Market. From Fortune Business Insights: https://www.fortunebusinessinsights.com/europe-data-privacy-software-market-107455
- George, M. (2025, May 13). GDPR Compliance: your guide to European data privacy regulations. From Ketch: https://www.ketch.com/regulatory-compliance/general-data-protection-regulation-gdgdpr
- Harri Insider Team. (2024, Jly 2). Understanding GDPR and Data Protection in Hotel and Restaurant Management. From Harri: https://resources.harri.com/blog/gdpr-compliance-hospitality-sector/
- Horizon Grand View Research. (n.d.). Europe Privacy Management Software Market Size & Outlook. From Horizon Grand View Research: https://www.grandviewresearch.com/horizon/outlook/privacy-management-software-market/europe
- Lindberg, M. (2025, February 6). European GDPR fines down 33% in 2024, but enforcement ‘remains dynamic'. From Grip: https://www.grip.globalrelay.com/european-gdpr-fines-down-33-in-2024-but-enforcement-remains-dynamic/
- Mee, B., Kirwan, M., Clarke, N., Tanaka, A., Manaloto, L., Halpin, E., . . . McElvaney, N. G. (2021). What GDPR and the Health Research Regulations (HRRs) mean for Ireland: a research perspective. Ir J Med Sci, 190, 505-514. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-020-02330-3
- Myśliwiec, J. (n.d.). Understanding GDPR: What It Means for Companies Working with B2B Data. From Infobel Pro: https://www.infobelpro.com/en/blog/understanding-gdpr-what-it-means-for-companies-working-with-b2b-data
- Nambiar, S. R. (2025, June 2). 5 GDPR Non-Compliance Risks You Can't Ignore. From CookieYes Blog: https://www.cookieyes.com/blog/gdpr-non-compliance/
- Neumetric. (n.d.). GDPR Penalties: What Businesses Need to Know About Non-Compliance Fines. From Neumetric: https://www.neumetric.com/journal/gdpr-penalties-need-know-non-compliance-fines/
- O'Dea, A. (2025, May 22). Seven years on businesses still grapple with GDPR compliance. From Silicon Republic: https://www.siliconrepublic.com/enterprise/seven-years-on-businesses-still-grapple-with-gdpr-compliance
- Practical Law Data ProtectionOpens in a new window. (2025, April 25). EDPB publishes 2024 Annual Report. From Practical Law UK: https://uk.practicallaw.thomsonreuters.com/w-046-6771?transitionType=Default&contextData=(sc.Default)&firstPage=true
- Privacy Engine. (2024, December 31). GDPR Statistics Worldwide 2024. From Privacy Engine: https://www.privacyengine.io/gdpr-statistics-worldwide-2024/
- Professional Academy. (n.d.). Cybersecurity in the Irish Finance Industry: Challenges and Opportunities. From Professional Academy: https://www.ucd.ie/professionalacademy/resources/irish-finance-cybersecurity-challenges-opportunities/
- ProfileTree. (2025, June 9). Navigating AI and GDPR in Ireland: 6 Pitfalls to Avoid. From ProfileTree: https://profiletree.com/navigating-ai-and-gdpr-in-ireland-6-pitfalls-to-avoid/
- Rai, A. (2025, June). Ireland Data Center Market - Investment Analysis & Growth Opportunities 2024-2029. From Coherent Market Insights: https://www.coherentmarketinsights.com/industry-reports/privacy-management-software-market
- Research and Markets. (2025, March). RegTech Market Report 2025. From Research and Markets: https://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/5939382/regtech-market-report
- ResearchandMarkets.com. (2024). Ireland RegTech Business and Investment Opportunities Databook. From BusinessWire: https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20241211020011/en/Ireland-RegTech-Business-and-Investment-Opportunities-Databook-2024---18.7-CAGR-Forecast-During-2024-2029-with-Irish-RegTech-Market-Set-to-Reach-US%24790.67-Million-by-2029---ResearchAndMarkets.com
- Sadoian, L. (2025, January 8). GDPR: Penalties for Noncompliance and How to Avoid Them. From UPGuard: https://www.upguard.com/blog/gdpr-penalties-for-noncompliance
- Saxena, A. (2024, November 1). Compliance Q&A: How much does GDPR compliance cost? From Sprinto: https://sprinto.com/blog/gdpr-compliance-cost/
- Straits Research. (n.d.). GDPR Services Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report By Offerings (Solutions, Services), By Organization Size (Large Enterprise, Small Enterprise, Medium-sized Enterprises), By End-User Industry (Banking, Financial Services), and Insurance (BFSI), Tel. From Straits Research: https://straitsresearch.com/report/gdpr-services-market
- Tourism Ireland. (2025, February 25). Privacy Policy. From Tourism Ireland: https://www.tourismireland.com/privacy-policy
- Tourism NI. (n.d.). GDPR Considerations for Tourism Business Providers. From Tourism Northern Ireland: https://www.tourismni.com/business-guidance/sector/accommodation/accommodation-getting-started/legal-considerations/gdpr-considerations-for-tourism-business-providers/
- Vercara. (2024, December 16). New Vercara Research Reveals Impact of Trust in Brands Following Breaches, Concerns Around Outside Threats. From Vercara: https://vercara.digicert.com/news/new-vercara-research-reveals-impact-of-trust-in-brands-following-breaches-concerns-around-outside-threats


